
Quinolones
The quinolones, also known as the fluoroquinolones, are a synthetic, bactericidal antibacterial class with a broad-spectrum of activity. The quinolones can be used for difficult-to-treat urinary tract infections when other options are aren’t effective, hospital-acquired pneumonia, bacterial prostatitis, and even anthrax or plague.
ACTIONS
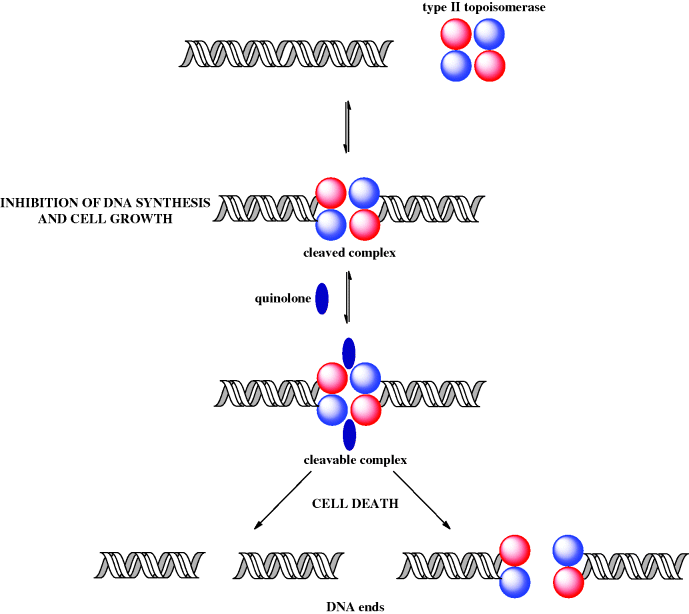
The fluoroquinolones exert their bactericidal (bacteria destroying) effect by interfering with an enzyme (DNA gyrase) needed by bacteria for the synthesis of DNA. This interference prevents cell reproduction, leading to death of the bacteria.

USES
The fluoroquinolones are used in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. The fluoroquinolones are effective in the treatment of infections caused by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. They are primarily used in the treatment of susceptible microorganisms in lower respiratory infections, infections of the skin, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin are available in ophthalmic forms for infections in the eyes.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Bacterial or fungal superinfections and pseudo membranouscolitis may occur with the use of both of these drugs. The administration of any drug may result in a hypersensitivity reaction, which can range from mild to severe and in some cases can be life threatening. Mild hypersensitivity reactions may onlyrequire discontinuing the drug, whereas the more serious reactions require immediate treatment. The more common adverse effects seen with the administration of these drugs include nausea, diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain or discomfort, and dizziness. A more serious adverse reaction seen with the administration of the fluoroquinolones, especially lomefloxacin and sparfloxacin, is a photosensitivity reaction. This is manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction when the skin is exposed to the ultraviolet rays of sunlight or sunlamps.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The fluoroquinolones are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the fluoroquinolones, in children younger than 18 years, and in pregnant women (Pregnancy Category C). These drugs also are contraindicated in patients whose life-styles do not allow for adherence to the precautions regarding photosensitivity.
PRECAUTIONS
The fluoroquinolones are used cautiously in patients with renal impairment or a history of seizures, in geriatric patients, and in patients on dialysis.
INTERACTIONS
Concurrent use of the fluoroquinolones with theophylline causes an increase in serum theophylline levels. When used concurrently with cimetidine, the cimetidine may interfere with the elimination of the fluoroquinolones. Use of the fluoroquinolones with an oral anticoagulant may cause an increase in the effects of the oral coagulant. Administration of the fluoroquinolones with antacids, iron salts, or zinc will decrease absorption of the fluoroquinolones. There is a risk of seizures if fluoroquinolones are given with the NSAIDs. There is a risk of severe cardiac arrhythmias when the fluoroquinolones gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin are administered with drugs that increase the QT interval (eg, quinidine, procainamide, amiodarone, and sotalol).
The FDA issued a strong warning about this class in 2016. Familiar names in the fluoroquinolone class include:
-
ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
-
levofloxacin (Levaquin)
-
moxifloxacin (Avelox)
